Strainlabs choice of gateway is the Multitech Conduit. It is a robust and reliable router that is specifically designed for industrial IoT applications. It is versatile with a set of different connection options including 2G, 3G, 4G LTE and Wifi. Strainlabs provides firmware updates OtA (Over the Air) when necessary, providing our customers with a seamless “Plug n Play” experience for connectivity.
The ability to add custom extension cards, or “mCards”, extends the usage even further by making different types of communications available. Strainlabs utilizes this mCard-slot with a Strainlabs receiver card which enables the use of our proprietary protocol on the 2.4 GHz band and a capability to integrate in other routers. Our receiver card has been designed to handle a several hundreds of Strainlabs Bolts per router.
Even if the router can communicate with a great number of bolts, it can be wise to use several routers to minimize the risk of data loss in the event of a power out or due to other failure in case of accident or external damage. A rule of thumb is to say that the value of redundancy outweighs the money saved by using just one router when the number of bolts increases.
Schematic sketch of Strainlabs wireless IoT system for bolted joints monitoring. Both the preload measurement and the transmitting of data occurs wirelessly without manual involvement. With the number of sensors used in modern connected industries, it wouldn’t be feasible to connect to the bolts via cable.
Setup process
Installing Strainlabs System is surprisingly easy. The routers are delivered preconfigured and all that is needed is to plug it into the power outlet. If there are active Strainlabs Bolts in range, the router will automatically start transmitting the data to Strainlabs Analytics.
The two most common communication options are 4G LTE and Wifi. If 4G is used, the router comes with a SIM-card installed and ready to go. When using Wifi, the customer will need to provide the login credentials before the router is up and running.
- Placement: One important aspect during installation is the placement of the router. Depending on the environment (industrial building, underground mine, airport etc) the placement can have an effect on the signal integrity between the bolt and the router.
- Data handling: The router will receive data packets from all bolts within range and send them to the cloud. However, before the data is sent away, the data packets are saved locally in the router. This internal buffer keeps the data intact and stored in the event of a communication error between the router and Strainlabs Analytics. As soon as the connection is restored the data will be sent to the cloud, still retaining its correct timestamps.
- Multiple routers and duplicate packets: We recommend duplicate data rather than loosing data, which is why using multiple routers is good for redundancy. Should the same sends data packages to several routers it is handled and merged in our cloud application Strainlabs Analytics.
State of the art remote & wireless monitoring
Strainlabs System has been designed to suit most industrial applications with the ability to send packages of data as far as possible without consuming too much battery power. The bolts have one way communication for battery reasons and the router, which functions like a vacuum cleaner, collects all packages that reach it. Strainlabs Bolts sends data to routers up to 90 meters away with free line of sight. When there is a need to strengthen the signal due to obstacles or distance there are ways to enable that including for example optimizing the number of routers or the direction of the antenna.
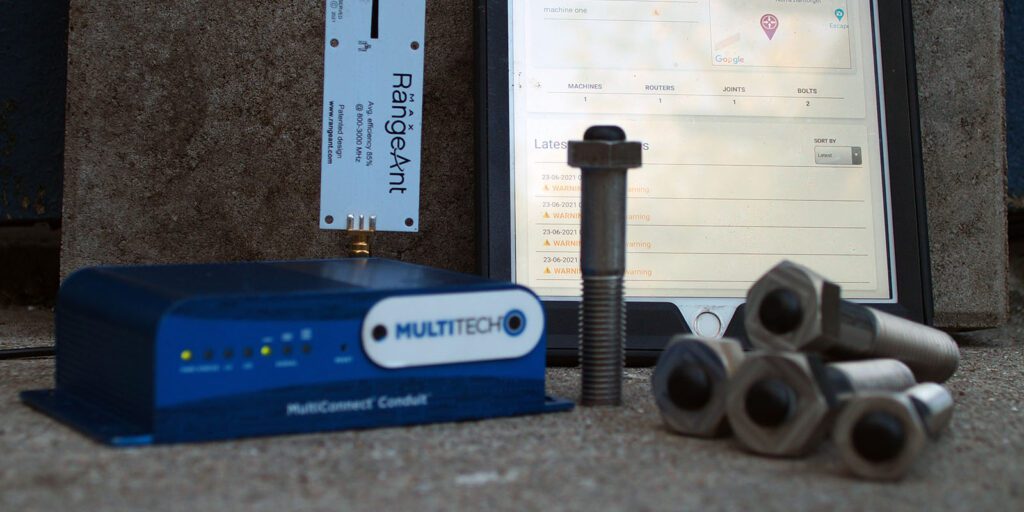

Strainlabs Router incorporates a custom receiver card and an antenna, specifically designed to receive, and forward data results from Strainlabs Bolts to Strainlabs Analytics.
Do you have the need for reliable monitoring? Contact us for an application review and demo of Strainlabs System. There are also additional and new technologies possible to look at together to find out the boundary conditions in radio communication and bolted joints.

