Strainlabs System with innovative IoT to utilize bolts when monitoring applications is part of enabling the next Industrial Revolution. Compared to the previous industrial revolutions that were sparked from mainly one new technology (steam engine, electrification, and computerization), this revolution is driven by a multitude of innovations including sensors technology like Strainlabs but also AI, Cloud, Augmented Reality, Additive Manufacturing, Virtual Reality and many more. Strainlabs CEO Csaba Madru explains: “Throughout the early years of researching feasible designs and the recent years of developing our system I’ve been impressed by the competence and specialist skills we’ve found in several of the rather small size companies we have collaborated with” says Csaba Madru.
Why are Strainlabs Bolts using 3D-printed metal?
“It was clear early on that we had quite high requirements on suppliers and one key component was particularly difficult to solve with traditional manufacturing” explains Csaba Madru. After considering a plastic material it was clear that metal would be preferred but the geometry was complex. Requirements further included a high ability to iterate the design, high strength and a fairly smooth surface. Combined with a need for high accuracy and manufacturing repeatability Strainlabs was guided to Digital Metal, a company located not far from Strainlabs office in south Sweden.
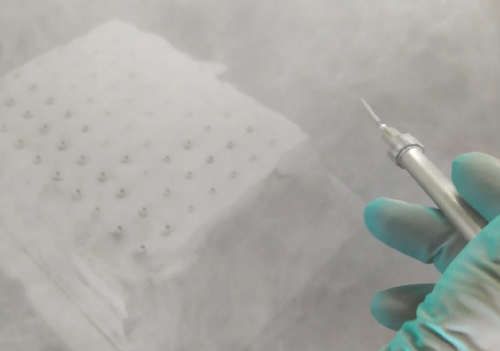
Alexander Sakratidis at Digital Metal explains: “Our additive manufacturing technique is perfect for advanced geometries of rather small key components. Often our technique replaces what would be multiple production steps and/or processes”.
Strainlabs design requires fine details and high precision in a way that traditional manufacturing techniques cannot meet.
The result
“Currently we need to meet customer requests in various ‘proof of concept’ orders for industrial leaders and we are also looking into a scale-up production phase with Digital Metal and other manufacturing partners” says Csaba Madru at Strainlabs. “With our high-precision binder jetting solution, we can follow our customers from the early iteration stages to high quantities and, as a last step, to delivering the printing system for a dedicated production line” explains Alexander Sakratidis. Further, the powder used in Digital Metal’s process is reusable which is Smart & Sustainable from a use-of-resource point of view which. This further adds to the reasons why digital 3D-printing is an important technique for Strainlabs long-term as it would be feasible also in high-volumes.